Cybersecurity is critical to protecting information, privacy, and critical infrastructure in the digital age. From an academic perspective, this article reviews the state of the art of cybersecurity, exploring its evolution, benefits and key tools, as well as scientometric indicators that reflect the development of research in this field.
In the academic field, cybersecurity has established itself as an essential discipline due to the growing complexity of cyber threats and the dependence on digital systems. Cybersecurity research not only focuses on the development of strategies and policies to protect information and communications, but also seeks to innovate technologies and methodologies that strengthen defense against cyber attacks.
Definition and Benefits of Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is defined as a comprehensive set of measures to ensure the security and continuity of operations in cyberspace. Its benefits are observed in various environments:
- Administrative: Protects the reputation and credibility of organizations.
- Financial: Prevents economic losses by avoiding data leaks.
- Technical: Assesses and mitigates cyber threats.
- Users: Guarantee the security of personal and professional information.
Within the modern definition of cybersecurity, there are three pillars, also known as the CIA triad: Confidentiality, Integrity and Access. Attacks on confidentiality are defined as the unauthorized disclosure of information. Integrity violations include unauthorized modification of information. Finally, when it comes to alterations to Access in cybersecurity, it refers to the unauthorized denial of use, reference or modification. A definition of the CIA triad regarding information security can be considered: certain information is secure if, and only if, all parties maintain its properties of confidentiality, integrity, and accessibility.
Evolution of scientific publications.
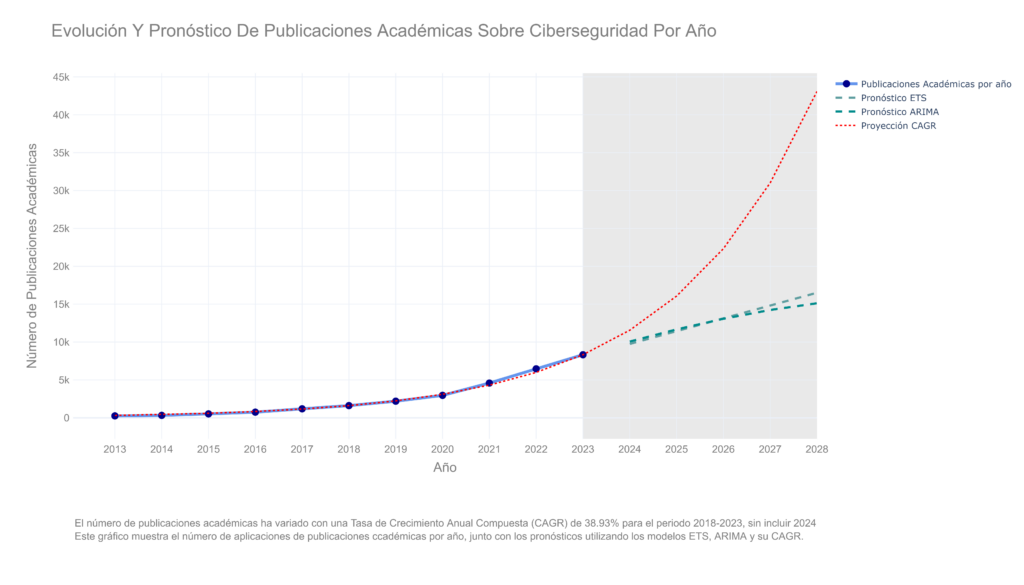
Academia not only serves as a catalyst for knowledge, but also plays an essential role in generating ideas and discoveries that, in turn, influence patenting activity in the industry. Scientific information in cybersecurity has experienced notable and constant growth in the last decade.
Instead of perceiving a period of abrupt multiplication in the number of publications, a constant increase in the production of knowledge in this field stands out, which goes hand in hand with the behavior in the issuance of patents. The close relationship between academic research and industrial innovation is evident. This connection underlines the importance of knowledge transfer, driving joint progress in research and innovation.
Geographic distribution of cybersecurity scientific production
Analyzing the geographical distribution of scientific publications is crucial to understanding
how different parts of the world contribute to the advancement of cybersecurity. The majority of academic research in cybersecurity is concentrated in the United States, possibly due to its jurisdiction's support and drive for innovation in this field.
India ranks second in scientific production, followed by China. The case of India illustrates how investment in research can facilitate technology transfer from academia to industry. This success can serve as a model for Latin American countries, urging them to promote research with technology transfer potential as a key strategy for their sustainable development.
Conclusions and recommendations
Cybersecurity, based on the principles of confidentiality, integrity and availability (CIA), is essential to protect digital information against threats such as phishing and malware, which can compromise data and network security.
Analysis of academic publications reveals steady growth in cybersecurity research over the past 10 years, with a predominant focus on cybersecurity strategies, hardware, software, and networks.
It is imperative that organizations recognize cybersecurity as a strategic priority and allocate adequate resources for its implementation and maintenance. This includes the adoption of advanced security tools and protocols, such as firewalls, antivirus and public key infrastructure (PKI) services, as well as the creation of specialized computer security incident response teams (CSIRT and SOC).



